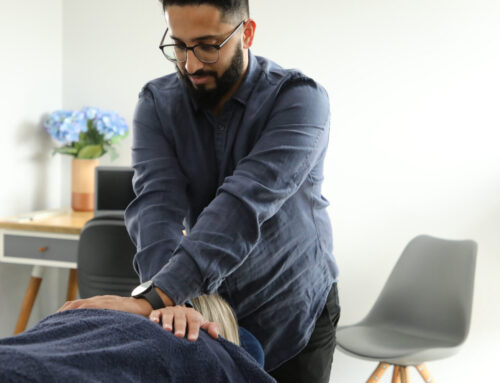
Are you suffering from lower back pain? You’re not alone! Did you know that four out of five people will experience lower back pain at some point in their lives? Lower back pain is a common reason our clients seek out osteopathic care.
As osteopaths, we take a holistic approach to treatment, and we consider how environmental and ergonomic factors may contribute to your back pain. Read on to find out about the different causes and treatment options for lower back pain!
Types of lower back pain and symptoms

Your lower back pain may be acute (i.e. lasts a few days or weeks), or chronic (i.e. pain that lasts for 3 months or longer). It might range in intensity from mild discomfort to severe pain that impacts your daily activities.
Common symptoms of lower back pain include:
- Sharp pain
- Dull/achy pain
- Pain that radiates down your glutes and thighs
- Pain that gets worse during activity or movement
- Pain that gets worse when sitting in the same position for extended periods
- Stiffness and decreased range of motion
- Postural issues
- Muscle spasms
It’s important to seek immediate medical advice if you have severe lower back pain that does not improve with rest, or lower back pain accompanied by numbness or tingling, lack of bladder or bowel control, fever, chest pain, or swelling in your back. This can be a sign of something more serious that may need urgent medical attention.
Common causes of lower back pain
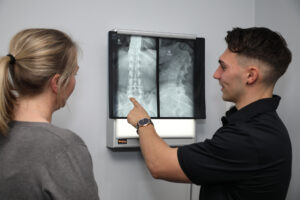 Lower back pain could be caused by something as simple as lifting something too heavy, twisting or bending awkwardly, or even sneezing!
Lower back pain could be caused by something as simple as lifting something too heavy, twisting or bending awkwardly, or even sneezing!
Conditions and diseases that commonly cause lower back pain, include:
- Sprains and strains: the most common cause of lower back pain
- Sacroiliac joint dysfunction: the joint may be tight or too mobile, causing pain that radiates into the glutes and thigh
- Disc injuries: bulging or herniated disc
- Sciatica: for example, a herniated disc presses on the sciatic nerve and pain radiates down the leg
- Osteoarthritis of the spine: inflammation of the joints causes pain and stiffness
- Spinal stenosis: a narrowing of the spinal column
- Fractures: can be caused by accidents or sometimes osteoarthritis
Preventing lower back pain
There are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of lower back pain or to prevent an injury from recurring. These include:
- Being active and exercising regularly, doing exercises that will strengthen your core muscles and help support your back
- Regularly doing back stretches
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on your spine
- Using proper lifting techniques
- Checking the ergonomic setup of your workspace
- Maintaining a good posture whilst at your desk
- Take regular breaks from sitting so that you are not in one position for an extended period
How can osteopathic treatment help?
At your initial appointment, we will gather information about your symptoms, relevant health and medical history, how the pain is impacting your daily activities, and consider any ergonomic or environmental influences. We will then conduct an osteopathic examination which may involve a series of movement tests to see if the pain is restricting your range of movement.
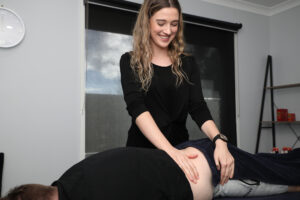
As osteopaths, we take an integrated approach to treatment. We will work with you to develop an individualised care plan. Depending on your symptoms and how they present, we may use some of the following treatment techniques:
- Physical manipulation, stretching and massage to increase mobility and relieve muscle tension
- Exercise and stretching programs
- Spinal manipulation
- Patient education
- Heat/ice therapy
If you need help managing lower back pain, come and see us. We are here to help! We will assess your symptoms and come up with a treatment plan to help relieve the pain. Call us on 5941-4157 or book online here.
References:
- Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Lower Back Pain. [Online]. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7936-lower-back-pain (Accessed 19 May 2022).
- NHS (2021). Osteopathy. [Online]. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/osteopathy/ (Accessed 19 May 2022).
- The Australian Family Physician (2021). Approach to low back pain – osteopathy. [Online]. Available at: https://www.racgp.org.au/afp/2014/april/osteopathy (Accessed 19 May 2022).
- Healthline (2019). What you should know about lower back pain. [Online]. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/low-back-pain-acute (Accessed 19 May 2022).